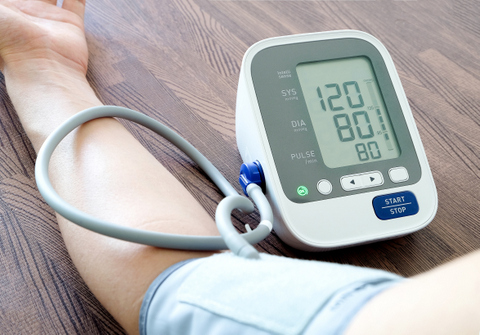
Self-monitoring of blood pressure at home is an important adjunct to clinic measurement because it provides supplementary information to practicing doctors.
Measuring your blood pressure at home means measurements can be done in your usual environment. It also allows for multiple readings to be averaged over time. Both of which give a more reproducible blood pressure values that are reflective of your "everyday" blood pressure.
This helps to mitigate abnormally high readings that sometimes happen due to anxiety when your blood pressure is taken in the clinic environment by a doctor or a nurse - also known as white coat hypertension.
Informed by home blood pressure readings, doctors can provide more accurate diagnosis and treatment of hypertension conditions to their patients.
Studies have also shown that patients who were trained to measure their own blood pressure at home may improve control of their blood pressure by improving drug compliance - since they become more involved and informed in their self-care.
There is now a plethora of devices that are developed with specific purposes and needs of users. Making sure the blood pressure monitor you choose is right for you can go a long way in ensuring your condition is well-managed and fuss-free.
Here are some pointers how you can start choosing one:
You may talk to your doctor or pharmacist as they will be able to help in selecting the most suitable type for you.
Blood pressure monitors vary in their inflation models - manual, semi-automatic or automatic.
Manual blood pressure monitors must be pumped up using a rubber bulb at the end of the cuff and have to be used together with a stethoscope to measure blood pressure. Correct use of manual monitors usually require medical training.
An automatic monitor also requires the cuff to be wrapped around your upper arm or wrist but automatically inflates by pressing a button, senses and records the blood pressure and displays the reading on a digital display on the monitor's screen. This is most accessible and common type for patients at home.
A wrong sized arm cuff or ‘miscuffing' can affect your readings. It is the biggest cause of inaccuracies in blood pressure measurement.
Measure around your bare arm halfway between your shoulder and elbow using a close measuring tape to find your size. Most upper-arm models have two sizes or a wide-range cuff that fits most people.
Make sure your upper arm circumference falls within the range of the blood pressure monitor cuff.
Most devices are sold with standard cuff sizes that will fit a majority of arms from the small adult to large adult range. Check the device specifications for the range of arm circumferences covered.
Children and adults with smaller or larger than average-sized arms may need special-sized cuffs. These optional cuffs are available from medical supply companies, by direct order from companies that manufacturer blood pressure cuffs, and in some pharmacies.
Make sure you can trust the readings that are shown on the blood pressure monitor.
Various standards and recognised protocols exist globally to measure the accuracy of automatic blood pressure measurement devices. Hence, make sure the device you have selected has been tested, validated and approved for accuracy by accredited bodies.
Validation bodies include the European Society of Hypertension (ESH), British Hypertension Society (BSH), or the Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation (AAMI).
dabl Educational Trust provides a good database of validated models that have been tested by the various standards.
A reputable device manufacturer will state whether their product adheres to an accredited standard on its packaging, if not, on their website.
You should also check if a monitor is still accurate after prolonged use. Manual blood pressure monitors require regular calibration while automatic monitors should be checked every once in a while - depending on the manufacturer.
Monitors vary in price depending on its brand and features. Some of the more expensive models may include features that you don't even need. Choose an appropriate blood pressure monitor that is suited for your use and needs.
Look for product comparison aids that are sometimes provided by manufacturers to help you in the selection process such as this one.
Buy a blood pressure monitor that is easy for home monitoring. Be sure the display on the monitor is easy to read and understand, and that the buttons are large and intuitive.
The directions for applying the cuff and operating the monitor correctly should be clear.
You should also consider its portability especially if you are a frequent traveller or are advised to measure your blood pressure several times a day. Look for the one that is compact and easy to bring around with.
To make your blood pressure routine as simple as possible, manufacturers have come out with various extra features that may benefit you.
Some of the additional features that you may consider include:
● Heart-related measurements: Measures pulse rate, detects an irregular heartbeat and tracks changes per second in your systolic or diastolic rates. Users tracking blood pressure to monitor potential heart conditions could benefit from these features, but they might be unnecessary for others.
● Connectivity: Some BP monitors can connect to your home computer so that the readings can be downloaded. More commonly now, there are BP monitors can connect via Bluetooth to your smartphone, which is very convenient when it works well. Some monitors even come with an app that helps you track, record and/or share your blood pressure readings with your doctor.
● Memory storage: Determine the needed memory storage based on how many times per day you need to take your blood pressure reading. You should also consider a multiple-user monitor if you and another family member will both be measuring your blood pressure regularly.
● Adjustable inflation level: The automatic inflation setting might be a lot higher than your systolic blood pressure, causing discomfort during the inflation. Some manufacturers allows you to adjust the inflation level or have in-built technology that automatically adjust the inflation pressure to each patient's condition.
Most reputable blood pressure monitors and cuffs come with a warranty that will guarantee the proper function of the monitor from 1 to 5 years.
Read the warranty options to know whether it covers the whole monitor or only the digital display or the actual monitor, but not the cuff.
Know that some brands will charge an additional fee for warranty activation while others offer the warranty free with the purchase of the monitor.
|
Previous article Going Nuts for the Heart |
Next article Daily Habits that can Help Lower Blood Pressure |